Table of contents
Treatment of Bone Loss in Teeth involves rebuilding bone strength and health that has been compromised due to periodontitis, the more serious form of gum disease.
Reversing this damage requires following an effective dental hygiene regime such as daily brushing and twice-daily flossing with antimicrobial toothpaste as a daily and twice daily regimen to remove plaque before it hardens into tartar and hardens into tartar deposits.

Treatment of Bone Loss in Teeth
Bone loss in teeth can stem from tooth loss, orthodontic changes, and diseases. It’s treatable through various procedures based on severity. Some treatments include:
- Flap surgery: Gums cut, folded to expose roots for better scaling, bone reshaping.
- Bone grafting: For periodontitis-caused root bone loss, graft from own or artificial/donated bone. It secures tooth, aids regrowth.
- Guided tissue regeneration: Encourages bacteria-damaged bone regrowth. Special fabric placed between bone and tooth.
- Composite bonding: Tooth-colored resin strengthens, enhances appearance, halts bone loss.
- Ridge augmentation: Rebuilds gum, bone tissue to hide defects, support implants, reshape teeth.
Consult your dentist for the best approach. Maintain good oral hygiene, increase calcium and vitamin D, avoid smoking, and have regular dental check-ups to prevent bone loss in teeth.
Dental Implants
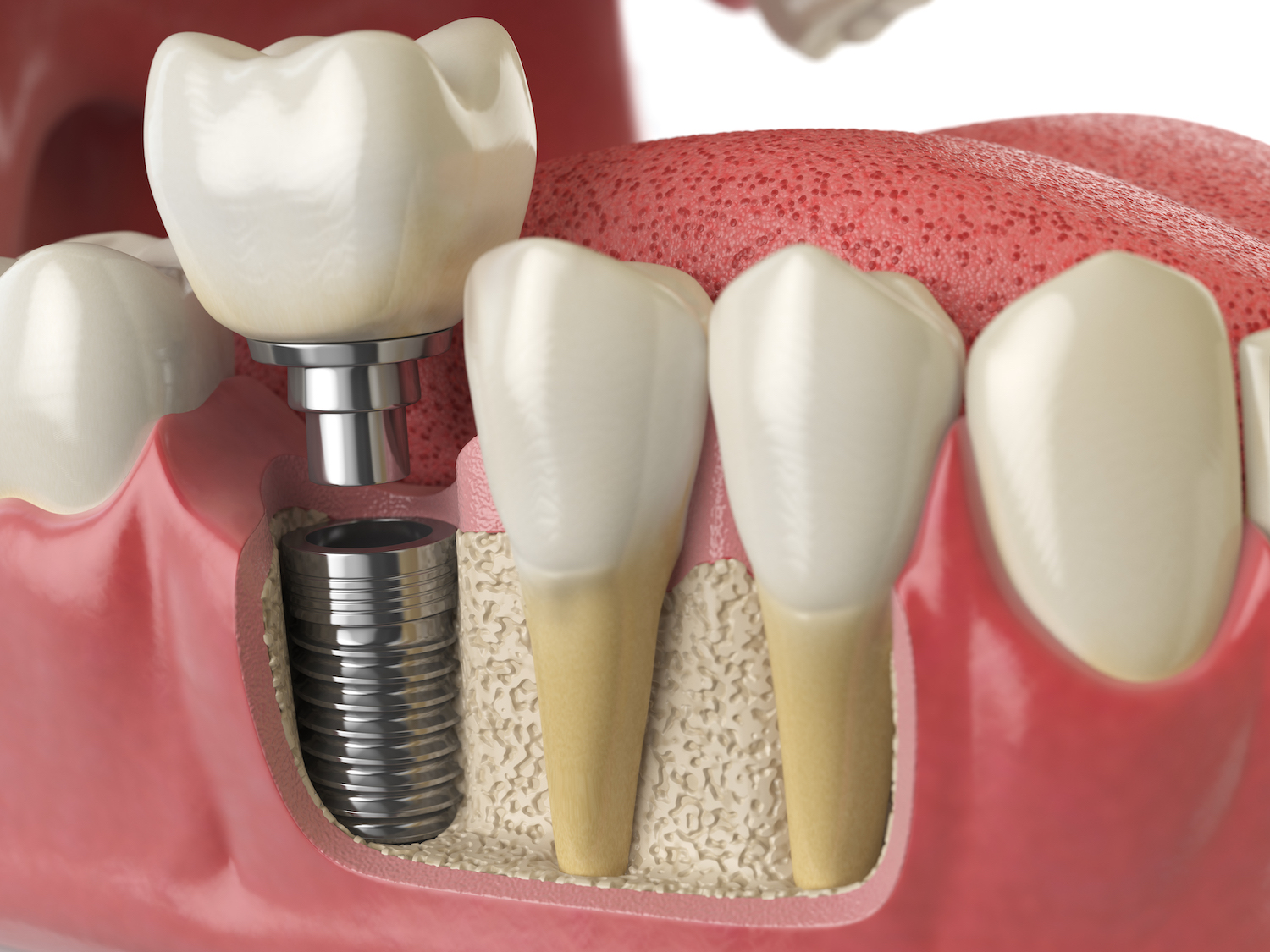
Dental implants are an innovative, long-term solution to missing teeth. Engineered to integrate seamlessly with your natural bone structure and provide support for artificial replacement teeth (crowns).
Key to any successful implant is having healthy jawbone tissue around which to place the tooth implant. When teeth are extracted without replacement, the supporting structures like jawbone shrink back into the body over time – thus increasing risk for further bone loss. Implants help stimulate new bone growth to protect against further loss.
Bone loss can also be accelerated by gum disease, with bacteria attacking and weakening tooth roots, weakening bone tissue. Implants are the only treatment option to both restore lost bone volume as well as stimulate new growth to protect natural teeth that remain.
Surgery to install dental implants may cause some discomfort during and after the process. Pain may be managed using prescription or over-the-counter pain relievers; any swelling of gums and face is normal but should subside within a few days.
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical process to stimulate bone formation. This may involve harvesting bone from another area of your own body (autograft), adding tissue from an animal (xenograft), or placing pieces from different animals’ jawbones as autograft.
Dental implants need sufficient bone and surrounding tissues for support, which must be treated. Otherwise, the area around a missing tooth will gradually resorb and weaken leading to implant failure and further complications.
Your dentist will open a flap to expose the alveolar bone underneath and insert graft material before stitching the wound closed.
Your doctor will recommend resting for four to six months in order to allow your body to heal completely, which includes refraining from smoking which hinders recovery, taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen and naproxen as these hinder recovery as well, instead opting for prescription-strength pain medication to manage any discomfort; typically dental bone grafts do not cause significant pain but swelling may be uncomfortable.
Periodontal Surgery
In cases where significant bone loss has already taken place, we employ various surgical techniques to promote natural bone regrowth. A bone graft involves placing small pieces of tissue between your bone and gum tissue sourced either directly from elsewhere in your mouth or from a tissue bank that has been thoroughly checked for disease.
At this appointment, we also use this procedure to remove bacteria from hard-to-reach areas of your mouth. In addition, loose teeth may need stabilization while their underlying bone heals – our specialists offer this service too!
At times, we can reverse periodontitis with laser technology known as LANAP. This dental technique uses laser technology to remove infections from gums and regenerate natural bone tissue. It has been thoroughly tested and proven safe. LANAP can especially beneficial in cases with severe bone loss as it stimulates your body’s natural ability to regrow new bone.
Teeth Whitening
Your jawbone continually remodels itself throughout your lifetime, replacing old bone with new through resorption – an innate process. However, if resorption occurs more rapidly than bone can produce new bone then jawbone will weaken and your teeth could loosen or even fall out.
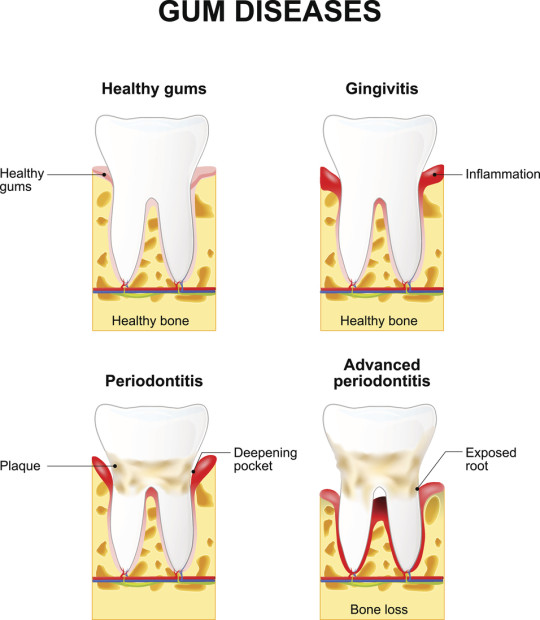
Periodontitis, commonly referred to as gum disease, is one of the main contributors to bone loss around teeth. This condition arises when bacteria buildup accumulates on and between teeth as well as within gum pockets resulting in pro-inflammatory states which destroy bone tissue surrounding each tooth and lead to loose or lost teeth.
Teeth whitening is an effective treatment option for discolored teeth that can help protect the health of both mouth and gums. This procedure uses high concentration hydrogen peroxide activated by light sources like laser or halogen lamps to enhance teeth whiteness; treatment typically lasts two or three weeks.

What Are the Causes of Bone Loss in Teeth
Bone loss in teeth can result from:
- Missing teeth: Jawbone lacks stimulation, leading to breakdown after tooth loss.
- Gum disease: Bacteria from periodontitis eat away underlying jawbone.
- Tooth infection: Untreated infection causes bone loss around tooth.
- Tumors and cysts: Jawbone can experience loss due to these growths.
- Prolonged tooth loss: Bone loss can occur from long-term tooth absence.
- Orthodontic adjustments: Adjustments may cause bone loss in teeth.
- Diseases: Osteoporosis, Paget’s disease can trigger tooth bone loss.
Good oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups crucial to prevent tooth bone loss.
Bone loss can also be caused by inadequate consumption of calcium, vitamin D or vitamin K in your diet; bruxism (grinding and clenching of your teeth); and TMJ disorder.
Bone loss may lead to larger gaps between teeth which become food traps for decay-causing bacteria – eventually necessitating costly dental treatments like root canal therapy or crowns as a solution.
How to Prevent Bone Loss in Teeth
Teeth are vital: they aid eating, facial structure, speech. Inadequate care weakens supporting bone. Prevent with these steps:
- Good oral hygiene: Brush, floss daily to remove plaque, prevent gum disease.
- Balanced diet: Calcium, vitamin D-rich foods like dairy, greens, fish support bone health.
- Limit sugar: Less sugary snacks, drinks to avoid tooth decay, gum disease, bone loss.
- Regular dentist visits: Detect bone loss early, get proper treatment.
- Dental implants: Replace missing teeth, stimulate jawbone, prevent bone loss.
- Quit smoking: Smoking raises gum disease, jawbone bone loss risk.
- Manage health conditions: Osteoporosis, others contribute to bone loss. Consult healthcare provider.
These steps maintain tooth health, prevent bone loss. Seek dentist’s advice for personalized guidance.

Symptoms of Tooth Bone Loss
Symptoms vary based on severity. Common signs include:
– Loose teeth, tooth loss
– Altered bite
– Gum recession
– Painful chewing
– New gaps between teeth
– Shifting, loosening teeth
– Shrinking gums
– Persistent bad breath
– Swollen, bleeding gums
– Pus between teeth, gums
– Chewing discomfort
– Headaches, facial, jaw pain
Note: Bone loss may lack symptoms; regular dental check-ups crucial. Experience these symptoms? Consult dentist promptly to prevent further issues.
Conclusion
Teeth are an integral part of our bodies; they help us eat, shape our faces, and facilitate speech. Without proper care and maintenance of both the gums and teeth, the bone that supports them could weaken. To prevent this, visit your dentist regularly and have them professionally cleaned to keep your jawbone strong; additionally consuming foods rich in calcium will keep both strong.
Dental bone loss usually stems from periodontitis (gum disease), caused by plaque and bacteria accumulating on teeth and in gum pockets for extended periods. This leads to chronic pro-inflammatory states in the mouth that wear away at jaw bone, eventually causing its destruction and weakening.
Bone grafts can help patients stop active bone loss with an effective surgical solution known as bone grafting. A dentist will replace lost bone with either natural or synthetic material, enabling regeneration to save loose and damaged teeth.














