Table of contents
Blood clots in the brain can produce severe symptoms, including sudden weakness on one side of the body, confusion, vision issues and severe headaches. Prompt treatment is key for ensuring faster recovery and limiting permanent disabilities.
Thrombolytic drugs can typically be administered three to four and a half hours after symptoms appear, helping dissolve existing blood clots and treat them more rapidly.

What is the Treatment for Blood Clot in Brain?
A brain blood clot is serious, potentially causing slurred speech, comprehension issues, heart attacks, and complications.
Treatment varies with clot type and severity. Options include:
– Anticoagulant meds: Prevent clotting, for history or stroke-related clots.
– Thrombolytics: Quickly dissolve clots in ischemic stroke.
– Mechanical thrombectomy: Surgical removal of disruptive clots impeding brain blood flow.
– Endovascular embolization: Encourages clotting.
– Stereotactic radiosurgery: Treats vascular malformations.
Early-stage clots respond well to treatment. For head injury with clot symptoms, seek immediate medical attention.
Standard Medical Procedures
The brain is an intricate organ that relies on constant blood flow to function optimally, so any blockages caused by blood clots in this vital organ can have serious repercussions for those affected by them. Anticoagulants (blood thinners) may be prescribed to combat such problems.
An infection of the brain can produce symptoms including slurred speech, weakness in one side of your body and stiff neck. If these are present for you, seek medical assistance immediately.
In cases of ischemic stroke, doctors employ alteplase (commonly referred to as tPA) injections within four and a half hours after an episode to restore normal blood flow and reduce damage from clot formation.
Other treatment options for an ischemic stroke may include surgery or inserting a filter inside the vena cava to help prevent more blood clots forming later on.
Medications
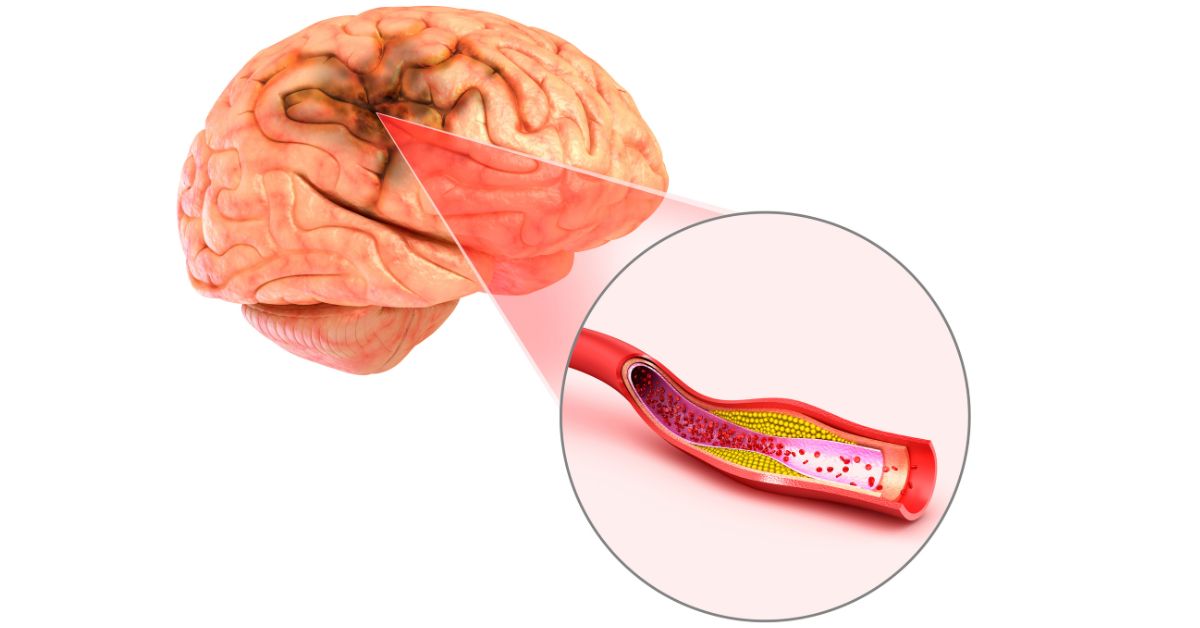
Blood clots are gel-like clumps of blood and other components that form when injured to stem blood loss and protect vital organs from damage. When they form in the brain or other parts of the body and block blood flow, however, this becomes a medical emergency; potentially causing seizures, stroke or permanent brain tissue damage as serious symptoms ensue.
Doctors treat brain clots through both medication and surgical interventions, including administering clot-busting drugs and blood thinners; surgical options include catheter-directed thrombolysis, mechanical thrombectomy and carotid endarterectomy.
After experiencing a TIA or minor stroke, doctors will typically give aspirin and an antiplatelet medication such as clopidogrel (Plavix) to lower your risk of another clot forming in your brain.
They may also recommend an anticoagulant such as unfractionated heparin to stop new clots forming while keeping existing ones from growing larger; these medicines change your blood’s chemical makeup to make it less sticky thereby decreasing future risk of clot formation.

Surgery
Blood clots that block brain blood vessels account for 87% of ischemic strokes; this condition is known as cerebral thrombosis. Broken-off blood clots may travel to other parts of the body where they impede blood flow and cause another form of stroke known as embolism.
Blood-thinning medications help prevent future blood clots by thinnining out the blood, giving people at risk or who have had one in the past. They may include blood thinners and anticoagulants.
Surgery may be used to treat blood clots in the brain. Mechanical thrombectomy involves doctors using a catheter with an attached device to grab hold of and extract the clot from a blocked blood vessel in your groin and the brain, similar to mechanical thrombectomy. Burr hole drainage involves creating small holes in your skull in order to drain away pressure on the brain more effectively.
Rehabilitation
An untreated blood clot in the brain can be deadly. Therefore, it’s vital that its symptoms be recognized quickly and that medical assistance be sought immediately.
Clot-busting medications are often the first course of treatment for a brain blood clot, though these should only be taken within three to four and a half hours after symptoms appear due to increased risks of bleeding complications.
Clot-dissolving medications may also be prescribed to help prevent future clots. Other treatments, like placing vena cava filters inside blood vessels in your body to filter clotted blood before it enters your brain, may help.
Surgery may be necessary to remove clots that obstruct blood flow to your brain, known as mechanical thrombectomy, through which a catheter is threaded through an artery in the groin until reaching its target clot in the brain, whereupon its straight wire coils into a corkscrew shape to grasp hold of it and remove it.

What Are the Risks Associated With Treating a Blood Clot in the Brain
When addressing brain blood clots, evaluating risks and key factors is essential. Prior to any treatment, understanding potential risks is crucial. Here, we outline risks linked to brain blood clot treatment:
Bleeding is a prime concern. Certain treatments, like thrombolytics, heighten bleeding risk, even within the brain, worsening stroke symptoms or causing complications.
Allergic reactions to clot treatment drugs, e.g., anticoagulants, are possible. Prior allergies or reactions to meds must be disclosed to healthcare providers.
Surgical risks arise in interventions. Surgery carries infection, bleeding, anesthesia issues, and possible harm to nearby tissues.
Medication side effects may manifest. Anticoagulants often lead to excessive bleeding, bruising, GI problems, and potential drug interactions.
Recurrence of clots post-treatment is plausible. If underlying causes (like clotting disorders) aren’t managed, brain blood clots can reoccur.
To make an informed choice on brain blood clot treatment, thorough consultation with healthcare professionals is vital. They offer tailored guidance based on your health history and situation.
How Long Does It Take To Recover From a Blood Clot in the Brain
The time it takes to recover from a brain blood clot varies due to factors like clot severity, health, and treatment.
– After hospital stay (3-4 days), home recovery lasts up to 12 weeks.
– Improvement occurs over months or years after brain clot.
– Post-surgery, expect 10-12 weeks for recovery.
Note that brain clot recovery is gradual, unique to each person. Rehabilitation and therapy aid function restoration. Healthcare pros’ guidance is key for optimal results.
Consult a healthcare pro for personalized info on brain blood clot recovery timelines.
What Are the Symptoms of a Blood Clot in the Brain
Symptoms of a brain blood clot vary based on location and severity. Here are common signs:
- Headache: Intense headaches, distinct from regular ones, can result from brain blood clots.
- Confusion: Clear thinking challenges, mental shifts accompany brain blood clot symptoms.
- Seizures: Clots may trigger seizures in certain instances.
- Speech issues: Slurred speech, word-finding problems can arise from brain blood clots.
- Vision trouble: Early brain clot indicator: blurred or darkened vision.
- Weakness/paralysis: One-sided face, arm, leg weakness/paralysis signals brain clot.
- Dizziness: Light-headedness, balance woes indicate a brain clot possibility.
- Nausea/vomiting: Brain clot can induce nausea and vomiting.
Remember, these symptoms can relate to other conditions like stroke or heart attack. If you notice these signs or suspect a brain clot, seek immediate medical help for diagnosis and treatment.














